How to Explain Different Biochemical Activity in Purified Enzyms
Richard Wolfenden Alumni Distinguished Professor of Biochemistry Biophysics and member of the National Academy of Sciences and co-author Charles Lewis PhD publish a report in the November issue of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences showing that without enzymes speeding the process it would take 23 bilion years to complete. 85 FACTORS AFFECTING ENZYME ACTIVITY Velocity or rate of enzymatic reaction is assessed by the rate of change in concentration of substrate or product at a given time duration.

Effect Of Temperature On Enzyme Activity Purified Enzyme Showed Download Scientific Diagram
Publisher Summary This chapter describes the development of methods for the assay of enzyme activity in a cell lysate or in a partially purified enzyme.

. Serial dilutions of an enzyme solution will have different enzyme activity values but identical specific activity values because in calculating specific activity the numerator unitsml and denominator. Protein purification is vital for the specification of the function structure and interactions of the protein of interest. A more practical and commonly used value is enzyme unit U 1 μmol min 1.
The concept of how a unique distinct key only can have the access to open a particular lock resembles how the specific. Influenzae is not a. The electrophoretic pattern indicated that the proteins were purified to homogeneity.
Protein purification is a series of processes intended to isolate one or a few proteins from a complex mixture usually cells tissues or whole organisms. The relationship between enzyme concentration and enzyme activity is directly proportional. Various factors which affect the activity of enzymes include.
You will compare and contrast the purification strategy for your enzyme to the purification strategy for lactate dehydrogenase LDH the enzyme purified in. On a graph showing reaction rate versus enzyme. Enzyme activity is a measure of the quantity of active enzyme present and is thus dependent on conditions which should be specified.
Solubility Change in pH Enzymes are least soluble at pIbecause there is no repulsive force between enzymes Enzyme must not be inactivated in a range of pH Change in ionic strength Large charged molecules are only slightly soluble in pure water. This intramolecular hydrolysis of asparagine to aspartic acid may explain the activity observed in this. 1 U corresponds to 1667 nanokatals.
But that was the case until James Sumner crystallized urease in 1926 1a development so revolutionary. This means that as the enzyme concentration decreases the reaction rate will decrease. The contamination of purified preparation with peptidoglycan was negligible and cannot explain the biological activities of purified preparation.
Addition of ion promotes solubility Salting in Beyond a certain ionic strength the charged molecules. This model considers the lock as an enzyme and the key as a substrate to explain this model. 1A and enzymes Fig.
The lock-and-key model is used to describe the catalytic enzyme activity based on the interaction between enzyme and substrate. In their presence reactions occur at rates that are a million 10 6 or more times faster than would be attainable in their absence. The results were different from those obtained with lipopolysaccharide but similar to those known from peptidoglycan studies.
Activities of the purified translation componentsWe evaluated the activities of the purified translation factors and enzymes except for RF1 RF3 and RRF from the reduction in protein synthesis. This chapter describes the development of methods for the assay of enzyme activity in a cell lysate or in a partially purified enzyme preparation which are also applicable during purification and for purified enzymes as well. The purification process may separate the protein and non-protein parts of the mixture and finally separate the.
Ie enzymes optimally active at 25 to 50C or psychrophilic enzymes ie enzymes optimally active at 5 to 25C. Different bacterial species make restriction enzymes that recognize different nucleotide sequences. When a restriction endonuclease recognizes a sequence it snips through the DNA molecule by catalyzing the hydrolysis splitting of a chemical bond by addition of a water molecule of the bond between adjacent nucleotides.
An enzymes shape is tied. Specific activity is an important measure of enzyme purity and values for different batches of a pure enzyme should be the same within normal experimental error. The reaction rates attained by enzymes are truly amazing.
We suggest that the phenol-water extract from H. Module 3 Enzyme purification. Breaking down food particles during digestion.
8 26 Methods of separation 3. Preincubation of the purified Asp-333--Asn mutant at 37 degrees C pH 8 however led to a complete recovery of activity and to a change of isoelectric point pI both of which are consistent with hydrolysis of Asn-333 to aspartic acid. Enzymes are biological catalysts also known as biocatalysts that speed up biochemical reactions in living organisms and which can be extracted from cells and then used to catalyse a wide range of commercially important processes.
Of the purified translation factors Fig. 12 APOBEC3 sub-family Over the past 100 million years APOBEC enzymes have evolved as a protective. Gazing at the three-dimensional structures of enzymes that regularly grace the covers of scientific publications it is hard to imagine that there are still people alive who remember when many biochemists thought that enzymes had no ordered structure.
The specific activity is a good indication of the purity and. In most biological environments the concentration of the enzyme is lower than the concentration of the substrate. The SI unit is the katal 1 katal 1 mol s 1 but this is an excessively large unit.
Unit U of enzyme activity is defined as the amount of enzyme that catalyzes the conver-sion of 1 μmol substrate per minute and its specific activity in U mg1 in crude extracts and after each purification step. Enzymes are produced naturally in the body and help with important tasks including. Enzyme activity as given in katal generally refers.
You will choose an enzyme for which you will design a purification strategy. Enzymes are biological catalysts and nearly all of them are proteins. These processes are essential in efficient immune defense against pathogens.
These enzymes were purified and screened for activity against oxidized and canonical nucleoside triphosphates and diphosphates substrate abbreviations found in Supplementary Table 1 using a. I once expressed in mesophilic hosts thermophilic and hyperthermophilic enzymes are easier to purify by heat treatment ii their thermostability is associated with a higher resistance to chemical denaturants such as a solvent or guanidinium hydrochloride. Genes AID introduced uracils are processed in different DNA repair and recombination pathways leading to class switch recombination and somatic hypermutation 6 7.
This chapter covers the basic principles of enzymology such as classification structure kinetics and inhibition and. What is even more amazing is that enzymes perform this function at body temperature 37C and physiological.

Enzyme Purification An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Molecular Weight Determination Of Purified Enzyme A Sds Page For Download Scientific Diagram
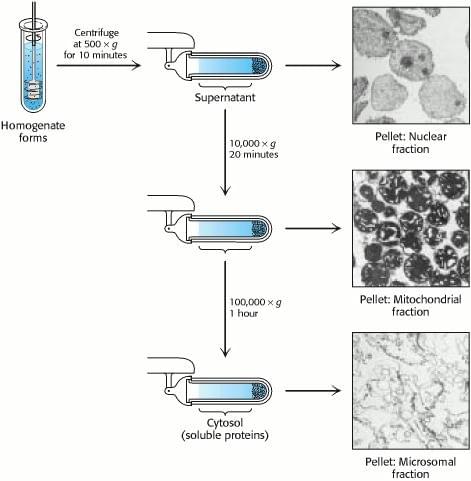
No comments for "How to Explain Different Biochemical Activity in Purified Enzyms"
Post a Comment